 Media Players
Media Players
Introduction
Modern browsers provide a default media player. Most have limited functionality to support accessibility.
Rather than coding all the things needed to make a player support accessibility, most organizations choose to use an existing player with good accessibility support.
There are players developed specifically for accessibility. Some are free, open source and some are commercial.
Skills Needed
Using an existing media player developed for accessibility requires moderate HTML skills.
Developing your own accessible media player requires advanced HTML and JavaScript skills.
Player Accessibility Functionality
Accessible media players provide a user interface that works without a mouse, through speech interface, when the page is zoomed larger, and with screen readers. For example, media players need to:
- Provide keyboard support (in Understanding WCAG: Keyboard Accessible)
- Make the keyboard focus indicator visible (in Understanding WCAG: Focus Visible)
- Provide clear labels (in Understanding WCAG: Labels or Instructions, Info and Relationships)
- Have sufficient contrast between colors for text, controls, and backgrounds (in Understanding WCAG: Contrast (Minimum), Contrast (Enhanced), Non-text Contrast)
Some media players provide additional accessibility functionality to users such as:
- Changing the speed of the video
- Setting how captions are displayed (e.g., text style, text size, colors, and position of the captions)
- Reading the captions with a screen reader and braille device
- Interactive transcripts
Interactive transcripts use the captions file. Interactive transcripts highlight text phrases as they are spoken. Users can select text in the transcript and go to that point in the video.
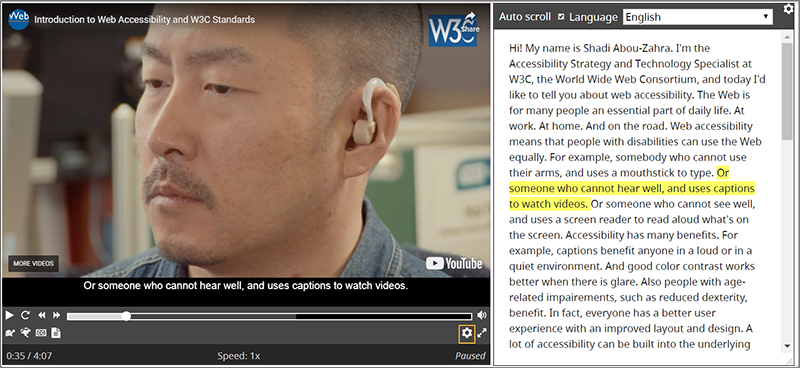
More details on player accessibility functionality are in a separate document: Media Accessibility User Requirements.
Existing Players
There is information online about the accessibility of media players. For example, Web-Based Media Player Accessibility Comparison Table (last updated July 2016) .
Each media player provides documentation of the steps to set it up in a web page. For example, AblePlayer Setup Steps .
Support for Description Methods
Media player functionality is required for some methods of providing audio description of visual information, as described in the Description page. To the best of our knowledge, the following media players provide such functionality:
- Supports description in text file (VTT format):
- AblePlayer — supports description when there is space in the audio, and when the video needs to pause (“extended description”)
- video.js — supports description when there is space in the audio; does not support description when the video needs to pause (“extended description”)
- Supports separate audio file with description:
- AblePlayer
- OzPlayer
- video.js — with plug-in
(If you know of other players that provide that functionality, please let us know via GitHub or e-mail with the links in Help improve this page below. Thanks!)
Back to Top